(Device images from Samsung Gear VR and HTC Vive webpages)
Several years ago, virtual reality head-mounted displays (HMD) meant an expensive technology only available for certain research groups or leading companies.
However, in the last two years this virtual technology has taken a huge leap and has become more accessible to those interested. From the Google Cardboard, with prices starting at €5 to €6 to the newly HTC Vive Pro, whose starter kit has a price of around €1,000, it is possible to find a wide range of head-mounted displays, with different prices and specifications. The right choice must be a trade-off between your needs and price you would like to pay for them.
This wide offering is led by two brands that became the leading providers of virtual visualization technology: Samsung and HTC Corporation. There are very big differences between them when searching for an HMD, so a comparison is helpful, so let’s consider their specifications and applications.
SAMSUNG GEAR VR
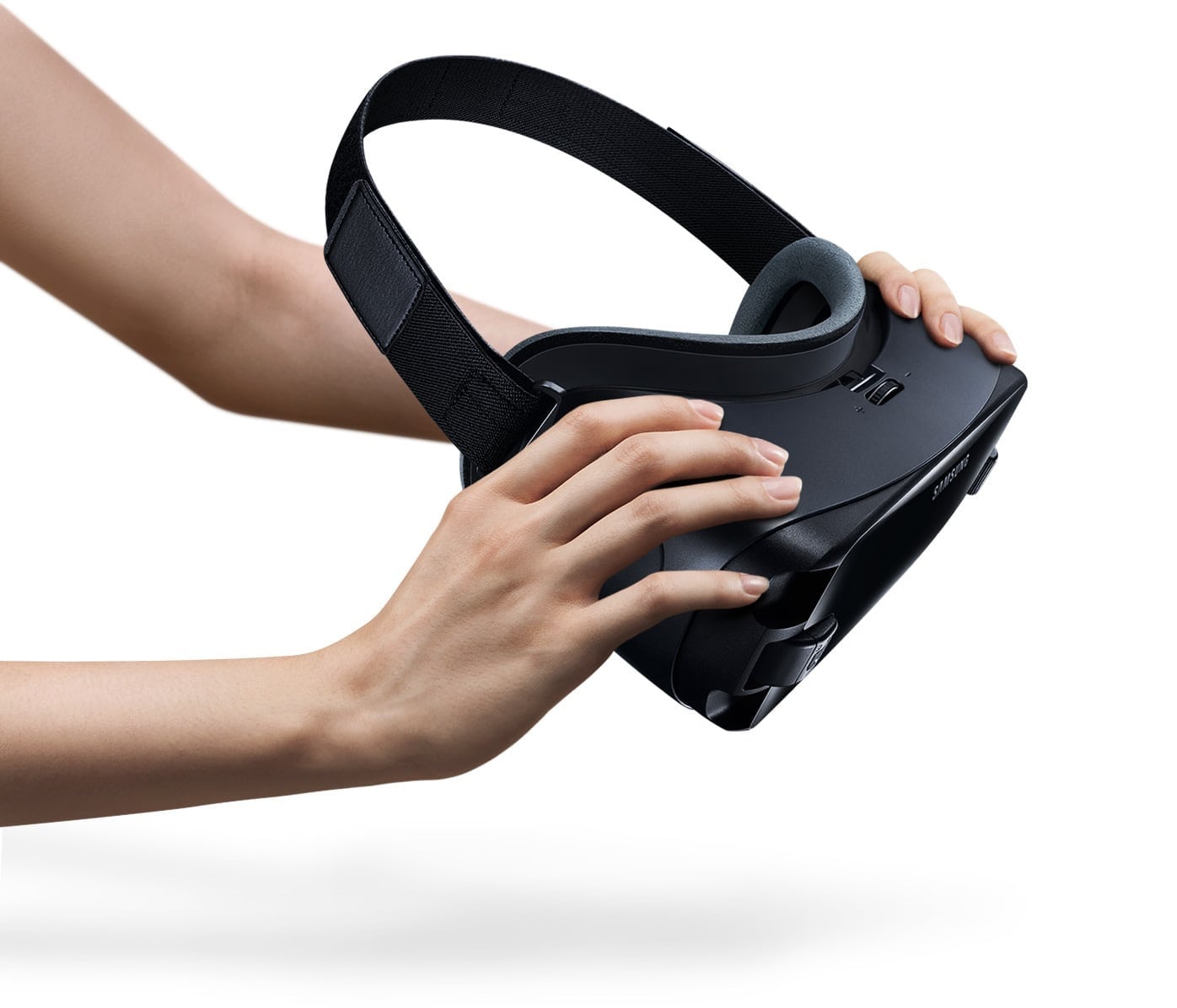
This HMD is based on the use of a mobile phone as hardware platform to run the applications, games or 360-degree videos. The Gear VR has evolved to this latest version, with less weight, a most convenient design and remote control for an easy-to-use navigation and interaction. In our review we will consider the latest version of Gear VR with an Oculus-powered controller.
(Image from the Samsung Gear VR webpage)
This device is not supported by all smartphones. The list of supported models includes Galaxy Note 9, S9, S9+, Note 8, S8, S8+, S7, S7 edge, Note 5, S6 edge+, S6, S6 edge, A8 Star, A8, A8+. Since USB ports are evolving with the technology, Samsung Gear VR is compatible with Micro USB and USB Type-C.
The main specifications of this device include, according to the manufacturer:
Field of view of 101°
Weight of 345g
Includes gyro sensor and proximity sensor
Bluetooth 4.2 BLE
The screen resolution depends on the smartphone
Compatible with Android Lollipop 5.0 or later
Price for the latest version: €129
HTC VIVE VR
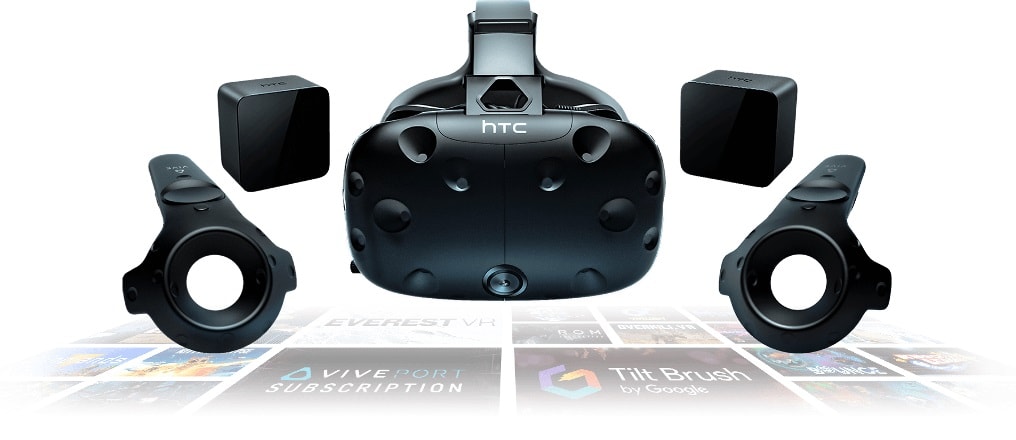
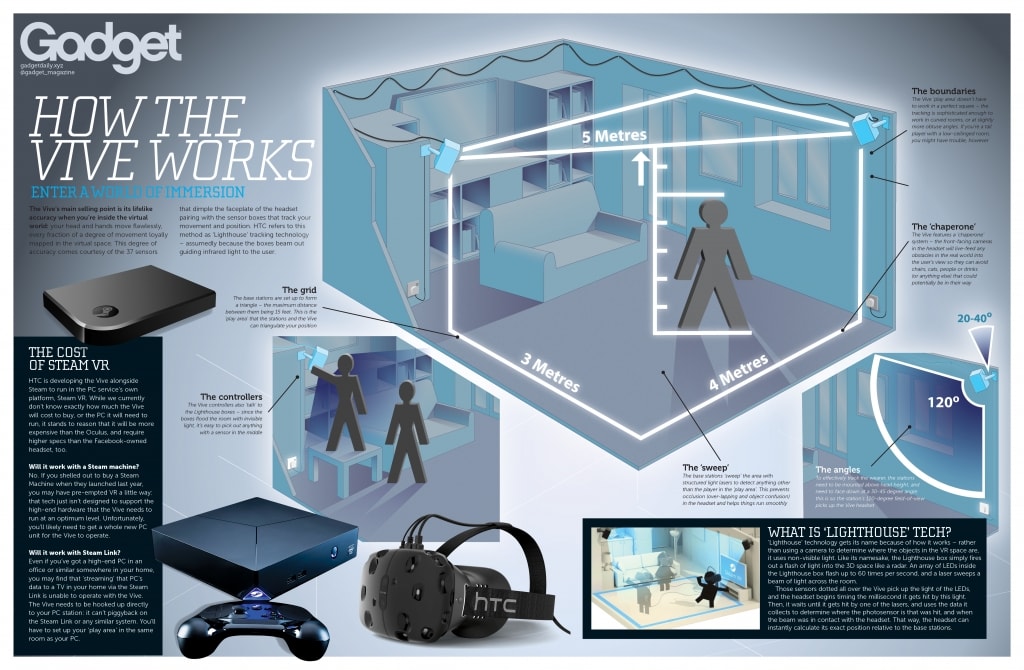
The HTC Vive offers currently two HMD versions: HTC Vive VR and HTC Vive Pro. Our review will focus on HTC Vive VR, and not the most recent one – PRO one – due to its high price. The HTC Corporation’s HMD is based on a visualization display connected to a computer, where the application, game or video is played. With this device a 15’x15’ stage can be set to be immersed on. The device is fully immersive, with 360-degree controller and headset tracking, it provides also directional audio and HD haptic feedback with the controllers provided. The immersion level it is very high but completely safe, because inside the application or game, it is possible to see in the screen information about the boundaries of objects included in the playing area to warn about possible collisions.
(Image from the HTC Vive official website)
This device does not need a smartphone. In this case, it is connected to a computer and the high-resolution screen will help you to feel completely immersed in the virtual world. The interaction is done using two controllers, in an intuitive and easy to use way. To set up the area to play, there are two base stations which allow to cover the defined area, track the motion in 360° and enable a wireless syncing and connection with the computer.
The main specifications of this device include, according to the manufacturer:
Field of view of 110°
Weight of 470 g
SteamVR tracking, G-sensor, gyroscope and proximity sensors
HMDI, USB2.0, stereo 3.5mm headphone jack, power and Bluetooth connections
Integrated microphone
The screen resolution is 1080 x 1200 pixels per eye (2160 x 1200 pixels combined).
Price: around €450
SAMSUNG GEAR VR VS HTC VIVE VR
At this point of our review, you will be able to highlight some of the main differences between the two devices compared: price, hardware (smartphone/computer), weight and interactivity level.
Let’s review these competitive HMDs with more detail to know their differences.
In the previous table, we have compared some specific characteristics between Samsung Gear VR and HTC Vive VR. Let’s review in depth each characteristic to understand better the options and elements included in each HMD:
- Field of view
The field of view is the visible area with your eyes inside the HMD device. A wider field of view provides better results in terms of realism and immersion using the device. In this sense, the HTC Vive VR has a bit more field of view than the Samsung Gear VR, but not much.
Head tracking
Head tracking is the possibility of getting the motion of your head and change the visual information depending on its motion. It provides the possibility of looking around inside the virtual environment only by turning the head to each side. Both HMDs include this option.
(Image from Getty Images)
Integrated screen
This is one of the important differences between Samsung Gear and HTC Vive. The first does not include a screen, which is provided by the smartphone. The smartphone is integrated inside the HMD device using a specific compartment connected by a USB port. Conversely, the HTC Vive includes a screen inside the device, where the visual information is shown thanks to the HDMI connection to the computer.
Controllers
The point here is whether the device has any controller to interact with the environment. In this case the Samsung Gear has a very simple controller and HTC Vive has two: one for each hand, more complex and with lot of chances to create menus and different kind of interactions depending on the application.
(Images from HTC VIVE official web page and Samsung Gear VR official web page)
Gyro sensor
The gyro sensor enables the orientation of the device to be known, as well as measuring the angular rotation speed. Both Samsung and HTC include a gyroscope sensor.
Weight
The specific weight of the device.
Wireless
We compare the possibility of using the device without wires connected to the HMD, so it has more freedom. In this case Samsung Gear VR can be wireless because it uses the smartphone connected inside as the hardware to run the application. The HTC Vive must be connected to a computer to get the visual information, so it cannot work wirelessly. It is possible to convert the HTC Vive VR into a wireless device using a specific Vive Wireless adapter that allows this device to run without wires connected to the computer. The price of this adapter is €300.
(Wireless adapter from the HTC Vive official website)
Adjustable lenses
These allow the device to provide a better image and adapt it to a wide variety of users. Both devices include this option.
Accelerometer
The accelerometer is a sensor that measures the lineal acceleration of a device. It can detect if the device is in horizontal or vertical position. Both devices have an accelerometer sensor.
Position tracking
The position tracking gives information to the device about the movement of the person inside a certain interaction area. The motion is used to simulate the user movement inside the virtual environment. In this case only HTC Vive VR includes position tracking due to the base stations provided to set up a tracking area for the interaction with the virtual environment.
Stereo 3.5mm headphone jack
This connector allows standard headphones to be used to listen the sound while using the device. Only the HTC Vive VR includes this connector.
Integrated sound
The integrated sound allows the user to listen to the sound inside the virtual space without the need of headphones. Neither Samsung nor HTC have this option.
OLED screen
The OLED screen is a specific screen technology that offers a better image, wider fields of view and shorter response time than LCD screens. HTC Vive VR includes an OLED screen.
(HTC Vive OLED Screen Replacement from ifixit.com)
Laser-guided system
A technique to know the position of the objects inside a tracked area. For that purpose, the device uses laser emitters to fill the space with no visible light that allows the distance between objects to be accurately calculated. As a method to track the user position, only HTC Vive VR has this option.
Stereo speaker
Stereo speakers provide a better sound with independent channels for the right and left side. HTC Vive VR has this option.
Gesture control
The gesture control allows the device to recognize certain gestures to handle virtual objects in the simulated world. Only HTC Vive VR has this option.
Android compatible
The device is compatible with different Android devices. Samsung Gear VR has this option.
iOS compatible
The device is compatible with different iOS devices. Samsung Gear VR has this option.
POSITION TRACKING WITH HMD
To get a better immersion feeling in a virtual world it is very worthwhile to use position tracking, so the user has the feel of being in motion inside the virtual set. The market offers several motion tracking technologies: optical, electromagnetic…
The HTC Vive VR uses a laser system to calculate the distance between the objects, and uses it to follow the motion of the user and his/her closeness to the real objects in the tracked area. For that purpose, this device uses two base stations which cover the area with structured light lasers to detect all the objects included in it. In addition to early detection of possible collisions with close objects, it can triangulate the user position and follow his/her movement.
(image from Gadgetdaily webpage)
An alternative to this system is electromagnetic motion tracking, which allows the position of the user with reference to electromagnetic transmitter to be known. This enables the user to be tracked inside a specific area.
These systems can improve certain HMD without tracking position to get information about the user movement and modify the visual information according with it.
MORE INFORMATION
For more information about the differences between these HMD, please visit:
https://versus.com/es/htc-vive-vs-samsung-gear-vr (our review is based on this comparison)
https://www.gadgetdaily.xyz/heres-exactly-how-the-htc-vive-works/